tidyr
Principles of tidy data:
- Every column is a variable
- Every row is an observation
- Every cell is a single value
An example:
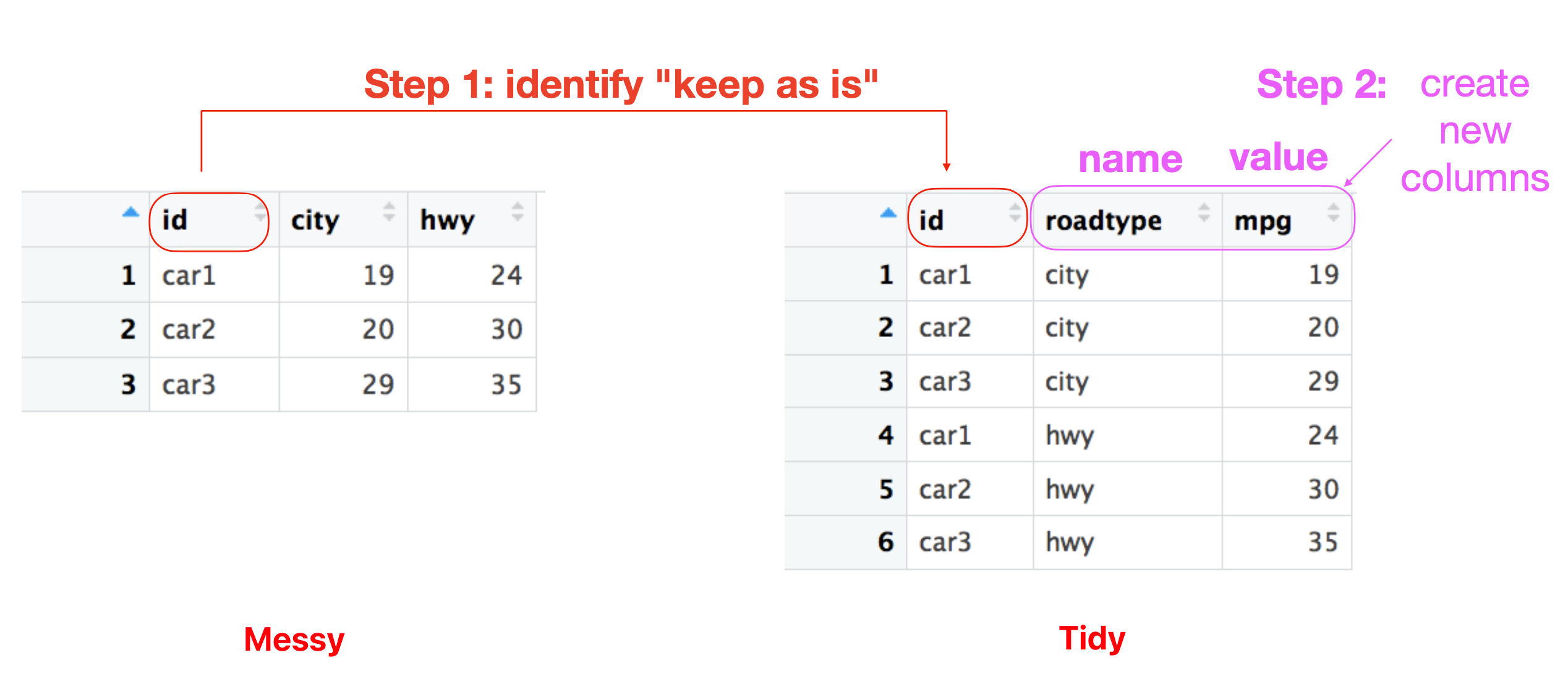
The code for this example using package tidyr is
tidydata <- messydata %>%
pivot_longer(cols = !id, names_to = "roadtype", values_to = "mpg")
pivot_longer()"lengthens" data, increasing the number of rows and decreasing the number of columns. The inverse transformation ispivot_wider()
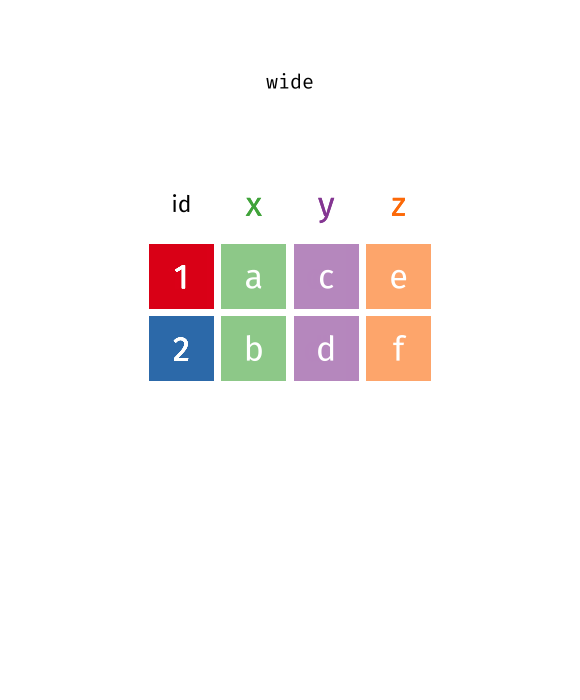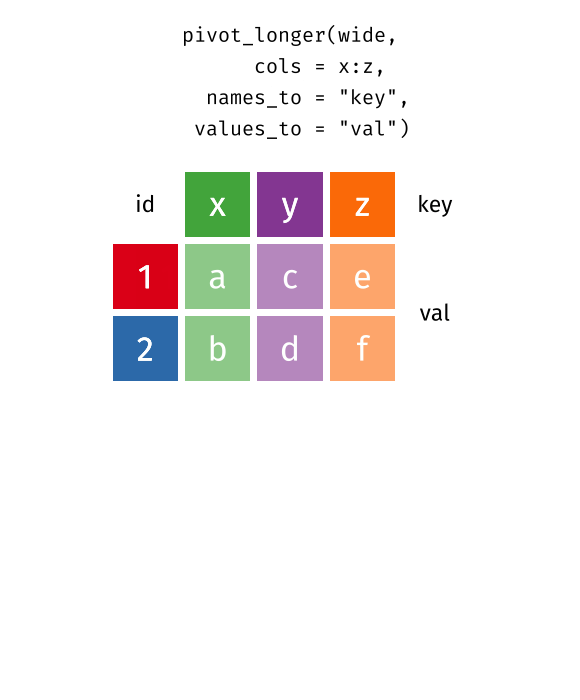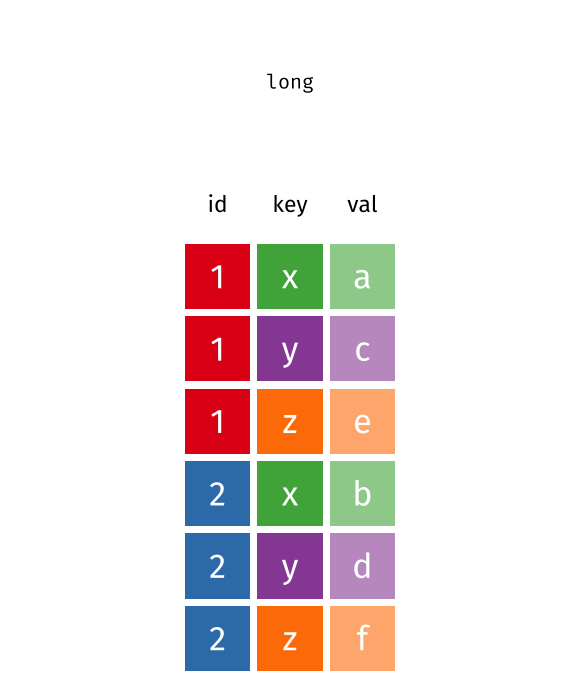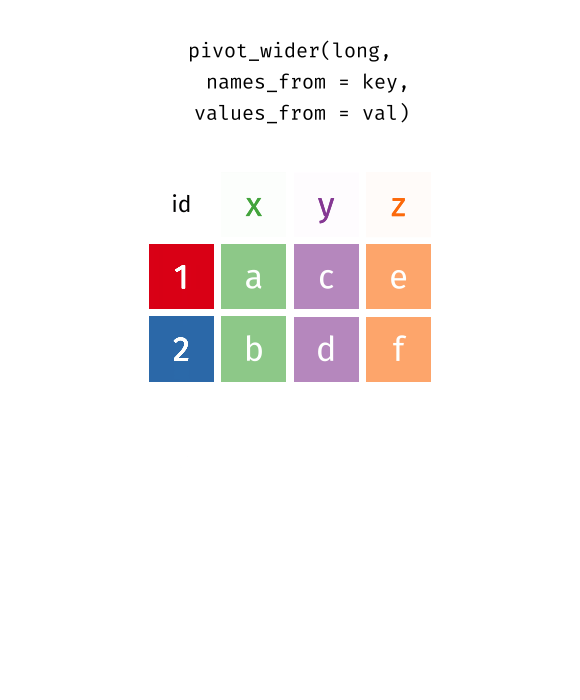
As we can see, the id column is essential. Sometimes data have row names, but don't have a column name for them. Then we can create one manually
library(tidyverse)
mtcars %>%
rownames_to_column("carname") %>%
head()
- "Tidy" or "messy" depends on the use case. Sometimes, "tidy" data can be "messy" in other scenarios.
 by zcysxy
by zcysxy